Comprehensive Guide: Stages of Wound Healing Explained
- Blog
- Blog Detail
Essential Stages of Wound Healing Explained for Better Recovery: A Comprehensive Guide

Mary Huntly APRN FNP-C
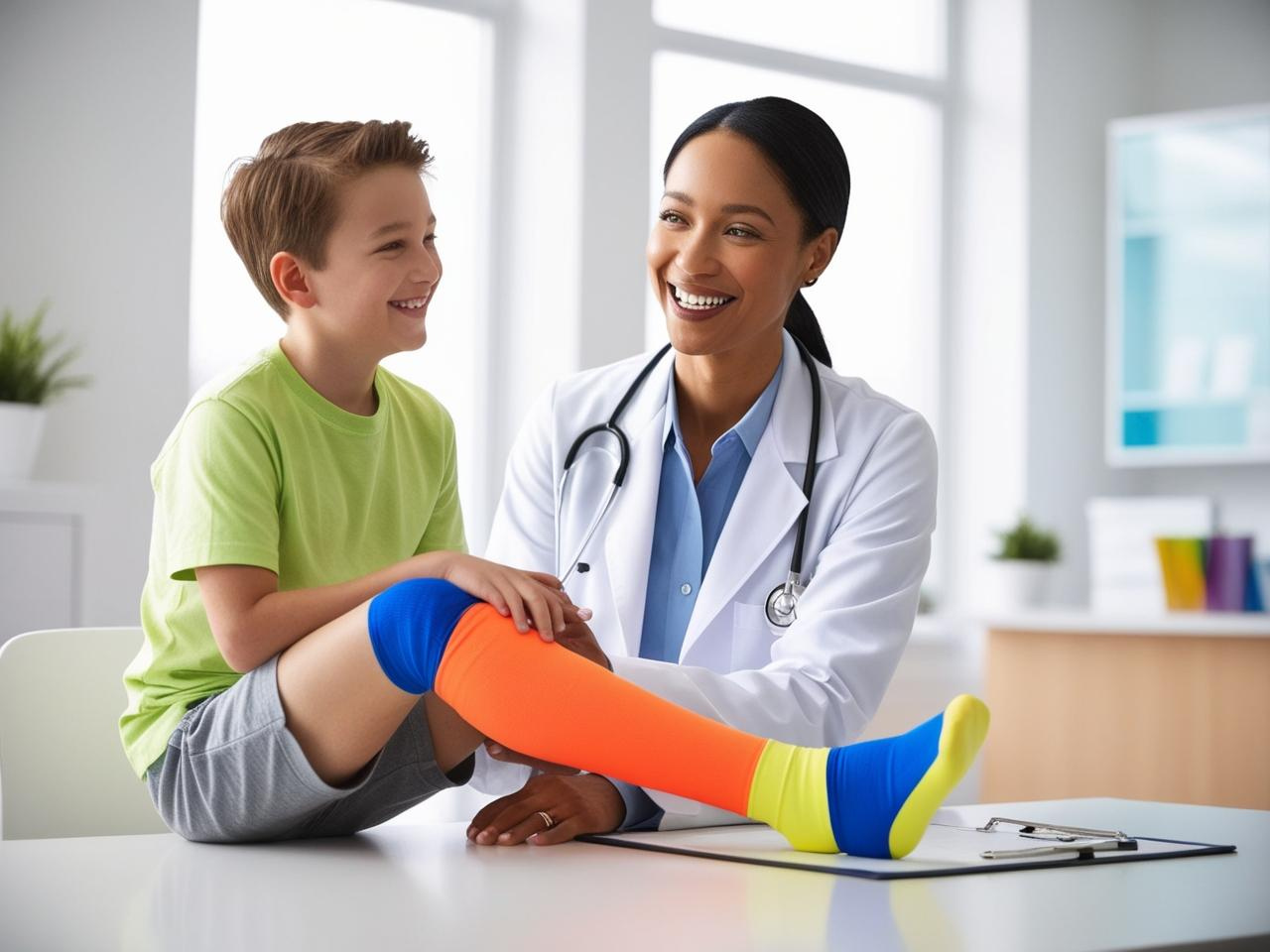
Ever wonder how your body heals a cut? It goes through four key stages: Hemostasis, Inflammatory, Proliferative, and Remodeling.
This article explains the “stages of wound healing explained,” so you can understand and appreciate how your body works to repair itself. We’ll dive into each stage to help you recognize what’s happening under the surface.
Key Takeaways
- Wound healing occurs in four key stages: Hemostasis, Inflammatory, Proliferative, and Remodeling, each essential for effective tissue repair.
- Proper wound care, adequate nutrition, and timely medical intervention are critical for promoting optimal healing and preventing complications.
- Chronic wounds may require advanced treatments, such as growth factor therapy and negative pressure wound therapy, to enhance recovery and improve patient outcomes.
Understanding the Wound Healing Process

The wound healing process is nothing short of a biological marvel. It is a finely tuned series of events that our bodies initiate in response to tissue injury.
This intricate process involves an array of cells, including:
- neutrophils
- macrophages
- lymphocytes
- keratinocytes
- fibroblasts
- endothelial cells
All working in unison to restore the integrity of the skin and underlying tissues.
Wound healing unfolds in four distinct yet interlinked stages: Hemostasis, Inflammatory, Proliferative, and Remodeling. Each stage is characterized by unique cellular activities and biochemical events that collectively drive the primary healing process and the wound healing phases. From the initial rush to stop bleeding to the final touches that strengthen the newly formed tissue, these stages are essential for effective wound repair.
Recognizing these stages is particularly important for managing chronic wounds or providing care to others in similar situations. Awareness of each phase helps us appreciate the importance of proper wound care and early interventions. We will explore each stage in detail to understand how this remarkable process unfolds.
1. Hemostasis Phase
The hemostasis phase marks the beginning of the wound healing journey. It is initiated immediately after the injury, with the primary goal of stopping the bleeding. This phase involves a rapid physiological reaction where blood vessels constrict to reduce blood flow, and a fibrin clot forms to seal the wound. The outpouring of lymphatic fluid and blood is a clear indication that the body is hard at work to achieve hemostasis.
Within a few minutes of the injury, this initial phase is usually completed. The cessation of bleeding signals that the hemostasis stage has successfully done its job. This crucial first step prepares the wound for the next phase: inflammation.
2. Inflammatory Phase
The inflammatory phase is the body’s second line of defense, kicking in right after hemostasis. This phase focuses on cleaning and stabilizing the wound to prevent infection. Key players in this stage include white blood cells and thrombocytes, which work tirelessly to remove debris and pathogens from the wound site.
During the inflammatory phase, symptoms such as swelling, redness, pain, and a clear liquid around the wound are common indicators. This phase usually lasts several days, during which the wound site undergoes a thorough cleaning process to create a stable environment for the next stage of healing.
3. Proliferative Phase
Tissue formation occurs during the proliferative phase. Typically lasting from 4 to 24 days, this phase involves the creation of new tissue to fill, define, and cover the wound. A hallmark of this phase is the formation of granulation tissue, comprising new blood vessels, collagen, and other extracellular matrix components.
New epithelial cells migrate across the wound bed, resulting in wound contraction and eventual closure. This process is vital for restoring the skin’s integrity and function, and is a key aspect of cutaneous wound healing. The success of this phase lays the foundation for the final stage: remodeling.
4. Remodeling Phase
The remodeling phase, also known as the maturation stage, is the final stretch of the wound healing process. This phase can last from three weeks to two years, depending on the wound’s severity and individual healing factors. During this time, the new tissue gradually strengthens and matures, achieving maximum tensile strength.
Progress in the remodeling phase is marked by the wound area becoming pink, wrinkled, or stretched as new collagen fibers are laid down and reorganized. This phase ensures that the wound is fully healed and the repaired tissue is as robust as possible, marking the end of the wound healing journey.
Recognizing Problems in the Wound Healing Stages
While the wound healing process is generally efficient, it can sometimes encounter problems that hinder its progress, including delayed primary wound healing. Early recognition of these issues is key for effective intervention. Chronic wounds, for instance, are those that fail to heal within 4 to 6 weeks despite appropriate treatment. These wounds often require timely medical intervention to prevent complications and promote healing.
Common signs that a wound is not healing properly include increased pain, persistent redness, and the presence of pus. Such symptoms may signal disruptions in the healing phases, leading to delays and poor outcomes. Recognizing these signs enables early detection and treatment, crucial for optimal wound healing.
To better understand these problems, we need to delve into specific issues like wound infections and persistent inflammation. These factors can significantly affect the healing process, resulting in chronic wounds and other complications. Let’s explore these issues in more detail.
Signs of Wound Infection
Wound infections are a common complication that can severely disrupt the healing process. Infections arise when microorganisms replicate at the wound site, triggering local tissue responses. Indicators of infection include excessive redness, increased pain, and the presence of pus around the wound.
Preventing infection is critical for proper wound healing. Simple steps like washing hands before treating a wound and covering it properly to shield it from dirt and bacteria can make a significant difference. Observing signs of infection like persistent redness and pus necessitates prompt medical intervention to prevent further complications.
Persistent Inflammation
Persistent or prolonged inflammation can signal that a wound is not healing properly. This condition may lead to a chronic state, preventing the wound from progressing through the normal healing stages. Prolonged inflammation often features recurring symptoms such as redness, swelling, and pain, indicating poor healing or infection.
Bacteria can exacerbate this issue by creating a protective slime that hinders healing by forming barriers and low-oxygen environments. Persistent symptoms of prolonged inflammation warrant medical advice to address underlying issues and promote healing.
Factors That Affect Wound Healing
Wound healing is influenced by a myriad of factors that can either promote or hinder the process. These factors can be broadly categorized into local and systemic factors. Recognizing these influences is crucial for effective wound management and optimal healing.
Local factors such as infection, oxygen levels, and foreign bodies at the wound site can significantly impact the healing process. A clean environment and consistent wound care are vital to prevent infections and promote healing. Proper moisture balance and appropriate temperature and humidity levels are also essential in wound healing.
Systemic factors, including age, nutrition, and underlying medical conditions, also profoundly affect wound healing. Stress can impair healing through hormonal and behavioral responses, making it another critical factor to consider. Addressing both local and systemic factors creates an environment conducive to effective and efficient wound healing.
Local Factors
Local factors play a pivotal role in the wound healing process. Oxygen, for instance, is essential for cell metabolism, energy production, infection prevention, angiogenesis, and tissue regeneration. Inadequate oxygenation can lead to delayed wound healing and increased susceptibility to infections.
Other local factors such as pressure, tissue edema, hypoxia, and maceration can also impair the healing process. Optimizing the wound environment by managing these local factors can significantly enhance healing and prevent complications.
Systemic Factors
Systemic factors encompass broader influences that affect the entire body and, consequently, the wound healing process. Age is a significant factor, with 85% of non-healing wounds occurring in individuals aged 65 and older. A balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins A and C, and zinc is essential for optimal wound repair and healing, especially in cases of poor wound healing.
Conditions like diabetes, obesity, high blood pressure, and vascular disease can slow down the healing process due to impaired vascular flow and increased infection risk. Stress also plays a role by disrupting immune responses and hormone levels, leading to delays in recovery.
Addressing these systemic factors is essential for promoting effective wound healing.
Promoting Optimal Wound Healing

Promoting optimal wound healing requires a combination of proper wound care, adequate nutrition, and timely medical intervention. Proper wound care prevents complications like infections and ensures a conducive healing environment. Nutritional support, including essential vitamins and minerals, is pivotal in tissue regeneration and repair.
Implementing these strategies significantly enhances the wound healing process and helps prevent chronic wounds. Recognizing when to seek medical help is crucial, as timely intervention can significantly impact the outcome.
We will explore the specifics of proper wound care, nutrition, and when to seek medical help.
Proper Wound Care
Effective wound care is the cornerstone of proper wound healing. Keeping wounds clean, moist, and covered is essential to promote healing and prevent infections. Applying antibiotic cream can further protect the wound from bacterial contamination. Wound dressings should create a moist environment, allow absorption of exudate, provide airflow, and prevent contamination while being impermeable to bacteria.
Proper wound care practices significantly promote healing, reduce the risk of complications, and ensure faster recovery. Adhering to these guidelines supports the body’s natural healing process, achieving optimal wound healing.
Nutrition for Healing
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in the wound healing process. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is critical for effective healing. Vitamins C, A, and E are particularly important as they contribute to collagen synthesis and maintain cellular integrity, which are vital for wound repair.
Malnutrition can severely impair healing and increase susceptibility to infections. Consulting a healthcare provider about your diet can optimize the healing process and ensure that all necessary nutrients are being consumed. Proper nutrition is a proactive way to enhance wound healing.
When to Seek Medical Help
Knowing when to seek medical help is crucial in managing wounds effectively. If a wound is taking too long to heal or shows signs of infection, such as increased pain, redness, or discharge, it is essential to talk to a doctor. Early recognition of these signs can prevent complications and ensure proper healing.
Wounds that are slow to heal require professional assessment. Medical professionals can offer targeted treatments and interventions to address underlying issues and promote healing. Timely medical help can significantly impact the healing process.
Advanced Treatments for Chronic Wounds
Chronic wounds pose significant challenges and often require advanced treatments to promote healing. Treatment of these wounds can incur substantial healthcare costs, exceeding $25 billion annually in the U.S. Patients with chronic wounds often face prolonged hospitalization and reduced quality of life due to complications.
Trinity Wound Care offers several advanced treatment options for managing chronic wounds. These include hyperbaric oxygen therapy, which accelerates healing by increasing oxygen supply to the wound area, and negative pressure wound therapy, which enhances blood flow and keeps the wound moist. Additionally, the use of amniotic membrane allografts can address specific patient needs.
One of the most promising advanced treatments is growth factor therapy, which uses proteins to promote tissue regeneration and repair. We will explore how this innovative therapy works.
Growth Factor Therapy
Growth factor therapy involves the application of specific proteins that enhance the wound healing process by promoting tissue regeneration and repair. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) is particularly effective in stimulating cell migration and proliferation, which are crucial for tissue healing.
Other growth factors, such as transforming growth factor (TGF) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), play essential roles in promoting angiogenesis and collagen synthesis during the healing process. These growth factors help create a conducive environment for wound repair, leading to faster and more effective healing.
Trinity Wound Care Can Help
If you’re struggling with chronic wounds or need expert wound care, Trinity Wound Care is here to help. Trinity Wound Care offers comprehensive and effective treatment for chronic wounds with a team of specialists from various fields. Our personalized treatment plans are tailored to individual needs, ensuring optimal care for each patient.
At Trinity Wound Care, we emphasize the importance of thorough wound evaluations to facilitate effective care. We encourage patients to schedule regular wound management visits to monitor and support their healing process. Our expert wound care clinic in Las Vegas, Nevada, is dedicated to helping patients through every stage of wound healing until full recovery.
Don’t let chronic wounds dictate your quality of life. Contact Trinity Wound Care today and take the first step towards optimal wound healing.
Summary
The wound healing process is a complex but fascinating journey that our bodies undertake in response to tissue injury. Understanding the stages of wound healing—hemostasis, inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling—can help us manage wounds more effectively and promote faster recovery. Recognizing problems such as infections and persistent inflammation early on is crucial for preventing complications and ensuring proper healing.
By addressing both local and systemic factors, implementing proper wound care practices, and maintaining a balanced diet, we can significantly enhance the wound healing process. Advanced treatments like growth factor therapy and the comprehensive care provided by Trinity Wound Care offer promising solutions for those dealing with chronic wounds. Take proactive steps in managing wounds and seek professional help to achieve the best possible outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main stages of the wound healing process?
The wound healing process consists of four main stages: hemostasis, inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling. Understanding these stages can enhance your approach to wound care and recovery.
How can I prevent wound infections?
To effectively prevent wound infections, maintain cleanliness by washing the wound and surrounding area, apply a proper dressing, and use antibiotic cream as needed. Always wash your hands before treating a wound and consult a healthcare professional if you notice any signs of infection.
What factors can affect wound healing?
Wound healing is significantly influenced by local factors, including oxygen levels and infection, as well as systemic factors such as age, nutrition, underlying medical conditions, and stress. Addressing these factors is essential for optimal recovery.
When should I seek medical help for a wound?
You should seek medical help for a wound if you notice signs of infection like increased pain, redness, or discharge, or if it is not healing properly. Prompt attention can prevent complications and ensure proper care.
What advanced treatments are available for chronic wounds?
Advanced treatments for chronic wounds include hyperbaric oxygen therapy, negative pressure wound therapy, amniotic membrane allografts, and growth factor therapy. These options can significantly enhance healing and improve outcomes for patients.
PERSONALIZED HEALTHCARE
Bringing Healthcare to Your Doorstep
Receive custom-tailored treatment plans that include initial care, ongoing follow-ups, and comprehensive treatment for underlying causes, delivered to you no matter where you reside.

About Us
Trinity Wound Care is dedicated to providing compassionate, comprehensive wound care and support services, ensuring every patient receives personalized treatment for optimal healing and well-being.
Quick Links
Contact Info
- (725) 205-2457
- admin@trinityhealthlv.com
- 6655 W. Sahara Ave A218, Las Vegas, NV 89146