Advanced Neuropathic Wound Care at Trinity
Enter Banner Content Here
Effective Strategies for Managing Neuropathic Wounds
 Neuropathic wounds result from nerve damage, commonly seen in diabetes patients. They form primarily due to pressure on insensate areas of the skin, particularly on the foot, where reduced sensation prevents pain feedback. These ulcers are a common complication in patients with peripheral neuropathy, especially those suffering from diabetes mellitus. The lack of sensation in the affected areas means that patients often do not notice minor injuries, which can quickly escalate into serious ulcers.
Neuropathic wounds result from nerve damage, commonly seen in diabetes patients. They form primarily due to pressure on insensate areas of the skin, particularly on the foot, where reduced sensation prevents pain feedback. These ulcers are a common complication in patients with peripheral neuropathy, especially those suffering from diabetes mellitus. The lack of sensation in the affected areas means that patients often do not notice minor injuries, which can quickly escalate into serious ulcers.
Early detection and comprehensive management are crucial. Neuropathic ulcers can lead to severe complications, including infections and ultimately limb amputation, if not promptly identified and treated. Effective management not only aids healing but also prevents further complications. Regular foot care and monitoring are critical strategies in preventing the development of these ulcers.
Recognizing the causes and symptoms of neuropathic wounds is the initial step in effective management. This guide will delve into the various aspects of neuropathic wounds, providing a detailed look at their causes, symptoms, and the best strategies for managing and preventing these challenging conditions.
Understanding Neuropathic Wounds
Neuropathic wounds predominantly affect the lower extremities, caused by pressure points due to the lack of sensation in insensate areas. These wounds are not only painful and debilitating but also pose significant risks if not managed properly. The prevalence of neuropathic ulcers is particularly high among individuals with nerve damage, especially those suffering from diabetes. Conditions such as HIV and certain cancers can also contribute to the development of neuropathic ulcers.
Peripheral artery disease can exacerbate the severity of neuropathic ulcers by limiting blood flow, making these wounds more challenging to heal. The combination of reduced blood flow and lack of sensation creates a perfect storm for wound development and complications. These wounds can quickly lead to serious infections and even amputations if not treated effectively.
Recognizing the underlying causes and symptoms of neuropathic wounds is vital for effective management. Learning about the conditions that lead to these wounds and how to identify them early allows patients and healthcare providers to implement effective treatment and prevention strategies.
Causes of Neuropathic Wounds
The primary causes of neuropathic wounds include:
- diabetes
- peripheral arterial disease
- nerve compression
- HIV
- cancer
- metabolic disorders
Diabetes is a significant condition associated with neuropathic ulceration, affecting up to 51% of patients. Neuropathic ulcers result from poor sensory function in the peripheral nervous system, leading to pressure-induced skin breakdown. Diminished sensation causes repeated stress on the feet, which can lead to the development of ulcers.
Factors contributing to nerve injury in diabetic patients include hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and oxidative stress. These factors, combined with mechanical stress on the feet, create a high risk for ulceration. Additionally, risk factors for developing neuropathic ulcers extend beyond diabetes to include obesity, increased age, and a history of foot ulcerations. Vascular impairment is also essential for the development of neuropathic ulcers if pressure points are not involved.
Approximately 15% of individuals with diabetes will experience a diabetic foot ulcer during their lifetime, highlighting the importance of understanding and managing these risk factors. Addressing the underlying causes and implementing preventative measures can significantly reduce the incidence of neuropathic ulcers.
Symptoms and Identification
Common symptoms of peripheral neuropathy include numbness and a lack of sensation, leading to an inability to feel pain in the affected areas. This lack of sensation is a major risk factor for the development of neuropathic ulcers, as patients are unaware of minor injuries that can escalate into serious wounds. Visible signs of neuropathic ulcers may include well-defined edges, callouses around the ulcers, and calloused blisters.
One common initial complaint of patients with neuropathic ulcers is finding blood in socks or on floors due to ulcer drainage. Early identification of these symptoms is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment, which can prevent complications and enhance healing outcomes.
Effective Strategies for Managing Neuropathic Wounds
Managing neuropathic foot ulcers effectively requires a combination of traditional wound care and advanced techniques. These chronic non-healing wounds are primarily caused by peripheral neuropathy, which reduces sensation and leads to pressure-induced skin breakdown. Neuropathic ulcers are most commonly seen in the foot and predominantly affect the lower extremities due to pressure points in insensate areas.
Conditions such as diabetes and peripheral artery disease can exacerbate the severity of neuropathic ulcers by limiting blood flow and increasing the risk of serious complications, including infections and amputations. The high prevalence of neuropathic ulcers among individuals with nerve damage, particularly those suffering from diabetes, underscores the importance of effective management strategies.
Managing neuropathic wounds effectively involves strategies such as proper diagnosis and treatment, debridement and infection control, offloading techniques, and a multidisciplinary approach. By addressing these aspects comprehensively, healthcare providers can promote healing and prevent further complications in patients with neuropathic ulcers.
Diagnostic Approaches for Neuropathic Wounds
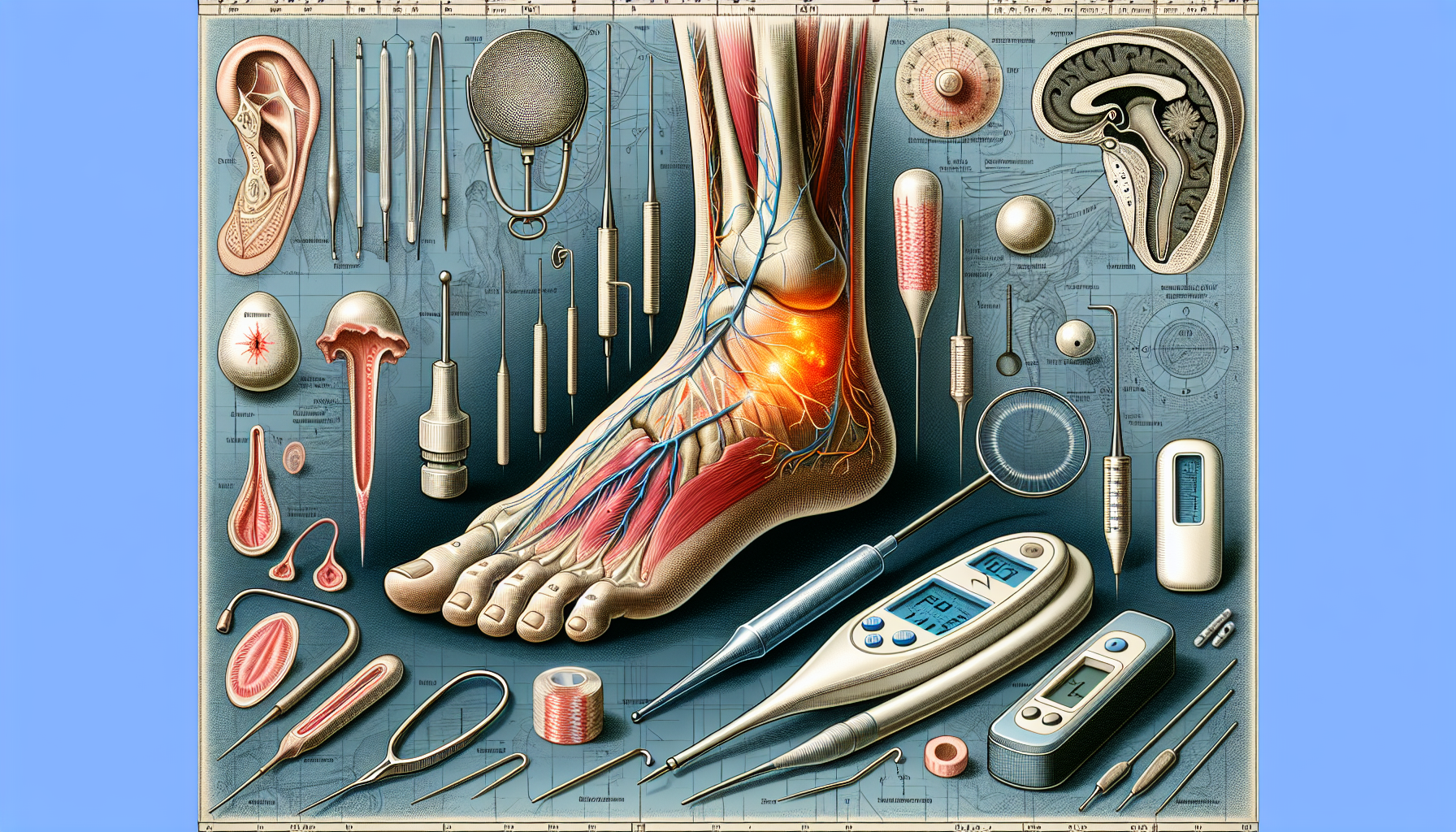
Accurate diagnosis and treatment of neuropathic ulcers are vital to prevent serious outcomes and enhance healing. Early recognition, thorough evaluation, and proven therapies are crucial for effectively managing neuropathic ulcers. Diagnosis often involves sensory nerves testing, such as monofilament or tuning fork tests, to assess the extent of nerve damage.
Early recognition and proper evaluation are crucial in the healing process of neuropathic ulcers. Understanding the diagnostic approaches for identifying these wounds helps healthcare providers implement early and appropriate treatment strategies, improving patient outcomes.
Clinical Examination
The clinical examination for diagnosing neuropathic ulcers involves a comprehensive review of the patient’s history, including the duration of neuropathy and any associated diagnoses. Physical examinations focus on the affected area, assessing ulcer severity and any associated wounds.
If a patient has a history of arterial disease, an ankle-brachial index (ABI) test using Doppler ultrasound is needed to evaluate adequate blood flow.
Advanced Diagnostic Tools
Advanced diagnostic tools play a critical role in assessing neuropathic wounds. Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (NCS/NCV) are utilized for electrodiagnostic testing. They help assess nerve function. Plain radiographs are performed to assess soft tissues, evaluate bone structure, and check for signs of osteomyelitis in neuropathic ulcerations.
Tests such as nerve conduction testing, vascular testing, and advanced imaging are essential for a thorough evaluation of neuropathic ulcers. In cases of suspected infection, microbiological swab tests and X-ray scans are utilized to confirm the presence of pathogens and assess bone involvement.
Treatment Strategies for Neuropathic Wounds
Managing neuropathic ulcers effectively often requires a combination of traditional wound care and advanced techniques. Treatment strategies must address the unique challenges posed by these chronic wounds, aiming to promote healing and prevent complications.
Effective treatment involves debridement and infection control, offloading techniques, and a multidisciplinary approach to ensure comprehensive care.
Debridement and Infection Control
Debridement is crucial in managing neuropathic wounds, as it prevents complications by removing dead tissue and assessing underlying infections. Infection control typically involves the application of topical antiseptics and antimicrobial agents to manage and prevent infections.
These practices promote wound healing and prevent infection spread.
Offloading Techniques
Offloading techniques are crucial in managing neuropathic wounds by relieving pressure on affected areas. A total contact cast (TCC) is often used to offload pressure from neuropathic ulcer sites while allowing for airflow to the wound. Footwear that provides adequate cushioning and support is also critical in preventing injuries that can lead to ulcers.
These techniques help to decrease pressure and promote healing in neuropathic wounds.
Multidisciplinary Approach
A comprehensive team for neuropathic ulcer treatment may include:
- A diabetes educator
- A podiatrist
- An endocrinologist
- A surgeon
- An infectious disease specialist
Trinity Wound Care leverages a multidisciplinary team approach to effectively manage neuropathic ulcers, enhancing patient recovery through comprehensive care strategies.
The team at Trinity Wound Care includes specialists from various fields, offering comprehensive treatment tailored to individual needs.
Preventative Measures and Patient Education

Patient education on proper foot care practices can significantly reduce the risk of developing neuropathic ulcers. Regular foot care and maintaining good blood sugar control are critical for preventing neuropathic ulcer recurrence.
Preventing neuropathic ulcers effectively involves maintaining good foot hygiene and regular inspections. These strategies are essential for promoting healing and preventing complications in patients with neuropathic wounds.
Regular Foot Examinations
Daily foot inspections are crucial for early detection of potential issues that may lead to foot ulceration. Self-examinations help identify minor injuries early, preventing them from developing into serious ulcers.
Patients should be advised to look for any changes or injuries on their feet during self-exams, using a mirror if necessary, and involving a family member or caregiver for assistance.
Proper Footwear and Care
Proper footwear and care are crucial to preventing neuropathic ulcers. Patients should avoid wearing barefoot and non-diabetic approved shoes to decrease the likelihood of neuropathic ulcerations. Maintaining foot hygiene, including regular washing and moisturizing, is vital to prevent skin breakdown.
Daily foot care routines help identify issues early and promote overall foot health.
Prognosis and Complications
Neuropathic wounds significantly impact patients’ quality of life, causing physical limitations and emotional distress. These wounds are often painless, which may lead to delayed treatment and increased risk of complications. Osteomyelitis and bone infection can occur with untreated neuropathic ulcers, leading to severe complications if infection spreads.
A diabetic foot ulcer raises the likelihood of amputation. It also leads to additional complications and a poorer prognosis. The 10-year mortality rate for patients with diabetic foot ulcers is 71%. Factors associated with increased early mortality in diabetic foot ulcer patients include a duration of diabetes greater than 10 years and a history of nephropathy.
Risk of Amputation
Diabetic foot ulcers are a primary cause of non-traumatic amputations, contributing to more than 80% of such procedures. About 14% to 24% of individuals with pedal ulcers may face the necessity of amputation. This risk is heightened by factors such as soft tissue infection, osteomyelitis, duration of ulceration, and vascular insufficiency. Up to one-third of patients diagnosed with a diabetic foot ulcer may require an amputation, highlighting the critical need for early and effective treatment.
The major complication associated with peripheral neuropathy affects amputation. Proper management and monitoring of foot ulcers can greatly reduce the risk of amputation, highlighting the importance of comprehensive care and patient adherence to treatment protocols involving peripheral nerves.
Long-term Management
Long-term management of neuropathic wounds requires appropriate supportive care tailored to individual patient needs. Regular follow-ups are crucial to monitor wound healing and adjust treatment strategies as needed. A multidisciplinary team can enhance the effectiveness of long-term care by addressing various aspects of patient health. Personalized treatment plans can significantly impact outcomes for patients with chronic neuropathic wounds.
Preventative strategies such as education about proper foot care are crucial for patients to avoid complications. Encouraging regular foot examinations can help detect issues early and prevent the progression of neuropathic wounds. Patient education on self-care routines and the importance of adherence to treatment can empower individuals in managing their conditions.
Trinity Wound Care’s Expertise
Trinity Wound Care employs an interprofessional approach to treating neuropathic ulcers, requiring consultation with specialists like podiatrists, general surgeons, and infectious disease experts. Their expert wound care staff is dedicated to treating neuropathic ulcers and wounds at their clinic, providing comprehensive and personalized care to each patient.
The team at Trinity Wound Care leverages their multidisciplinary approach to enhance patient recovery through comprehensive care strategies. By involving specialists from various fields, they ensure that each patient receives optimal treatment tailored to their unique needs.
Personalized Treatment Plans
Trinity Wound Care develops individualized treatment plans that consider each patient’s unique medical history, preferences, and specific needs, ensuring optimal healing outcomes. These personalized plans take into account factors such as the patient’s specific medical history and lifestyle, providing a holistic approach to wound care.
Individualized care plans at Trinity Wound Care focus on the unique needs of each patient, considering their medical history and specific ulcer characteristics. This personalized approach is crucial for effective diagnosis and treatment, promoting better healing outcomes and patient satisfaction.
Advanced Wound Care Techniques
At Trinity Wound Care, cutting-edge techniques are employed to ensure optimal wound healing. Advanced technologies such as bioengineered skin grafts and negative pressure wound therapy are utilized to enhance treatment effectiveness, reducing healing time and minimizing complications.
These innovations in wound care not only facilitate faster recovery but also contribute to better long-term outcomes for patients with chronic wounds. By employing advanced wound care techniques, Trinity Wound Care aims to improve the quality of life for their patients, promoting healing and preventing complications.
Summary
Neuropathic wounds pose significant challenges due to their complex nature and the severe complications they can lead to if not managed properly. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies is crucial for improving patient outcomes. Early diagnosis and comprehensive treatment, including debridement, infection control, offloading techniques, and a multidisciplinary approach, are essential for effectively healing neuropathic ulcers and preventing further complications.
Trinity Wound Care in Las Vegas offers expertise in managing neuropathic wounds through personalized treatment plans and advanced wound care techniques. By leveraging a multidisciplinary team and cutting-edge technologies, they ensure optimal healing outcomes and improved quality of life for their patients. If you or a loved one is dealing with neuropathic wounds, seeking expert care can make all the difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary causes of neuropathic wounds?
Neuropathic wounds are primarily caused by diabetes, peripheral arterial disease, nerve compression, and other conditions like HIV, cancer, and metabolic disorders. Notably, diabetes significantly affects up to 51% of individuals with neuropathic ulceration.
What are common symptoms of neuropathic ulcers?
Common symptoms of neuropathic ulcers include numbness and a lack of sensation in the affected areas, well-defined edges around the ulcers, callouses, and the presence of blood in socks or on surfaces due to drainage. These signs indicate significant underlying issues that require prompt attention.
How are neuropathic wounds diagnosed?
Neuropathic wounds are diagnosed through sensory testing, electromyography (EMG), nerve conduction studies, and imaging techniques like X-rays to evaluate infections and bone involvement. These assessments help determine the degree of nerve damage and the appropriate treatment plan.
What treatment strategies are effective for neuropathic wounds?
Effective treatment strategies for neuropathic wounds encompass debridement and infection control, offloading techniques such as total contact casts and appropriate footwear, and a multidisciplinary approach involving various specialists. Implementing these strategies is crucial for optimal healing outcomes.
How can neuropathic ulcers be prevented?
Neuropathic ulcers can be effectively prevented by educating patients on proper foot care, ensuring good blood sugar control, conducting regular foot inspections, wearing appropriate footwear, and maintaining foot hygiene. These practices are crucial in preventing skin breakdown and ulceration.
PERSONALIZED HEALTHCARE
Bringing Healthcare to Your Doorstep
Receive custom-tailored treatment plans that include initial care, ongoing follow-ups, and comprehensive treatment for underlying causes, delivered to you no matter where you reside.

About Us
Trinity Wound Care is dedicated to providing compassionate, comprehensive wound care and support services, ensuring every patient receives personalized treatment for optimal healing and well-being.
Quick Links
Contact Info
- (725) 205-2457
- admin@trinityhealthlv.com
- 6655 W. Sahara Ave A218, Las Vegas, NV 89146